Service hotline
+86 0755-83044319
release time:2025-05-16Author source:SlkorBrowse:7940
A chip etching machine is a specialized tool used in semiconductor manufacturing to selectively remove material from silicon wafers. This process, known as etching, creates intricate circuit patterns essential for modern electronics. The precision of a chip etching machine ensures components meet exact design specifications, making it indispensable in producing devices like smartphones and computers. Unlike traditional mechanical methods, advanced machines use plasma or chemical reactions for nanoscale accuracy. For example, companies such as Applied Materials and Lam Research dominate this field, offering systems that integrate automation for higher throughput. Learn more about semiconductor processes at Semiconductor Industry Association.
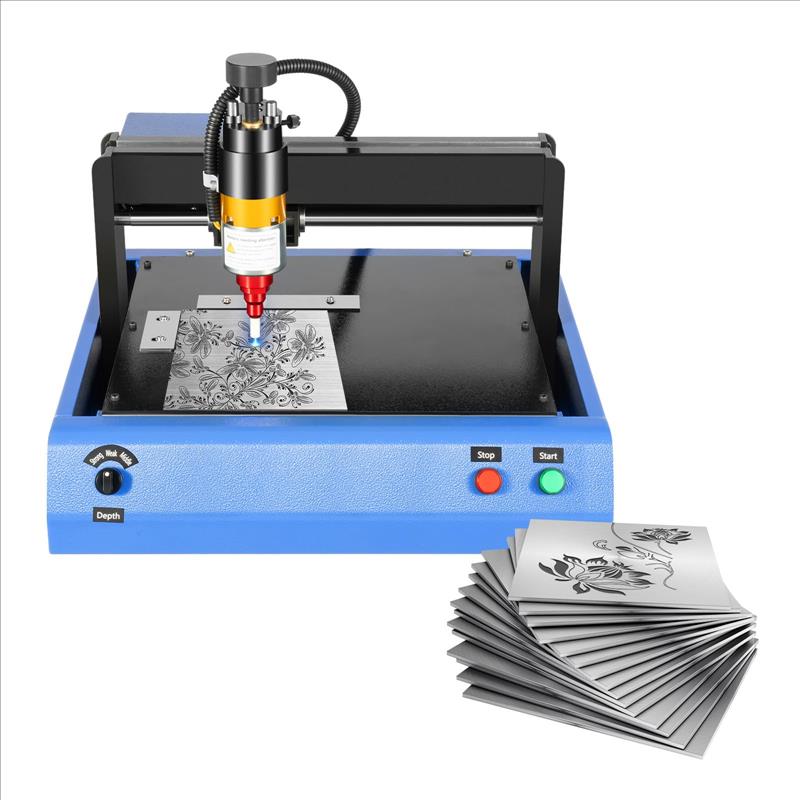

The evolution of chip etching machines mirrors advancements in semiconductor technology. In the 1960s, wet etching dominated, using liquid chemicals to dissolve unprotected silicon. However, the rise of integrated circuits demanded finer control, leading to dry etching techniques like reactive ion etching (RIE) in the 1980s. By the 2000s, plasma-based systems became standard, enabling sub-10nm precision. Today, innovations such as atomic layer etching (ALE) push boundaries further. This progression underscores how chip etching machine capabilities have shaped Moore’s Law, allowing transistors to shrink while performance soars.
Modern chip etching machines are defined by three core traits: precision, scalability, and versatility. Precision ensures minimal material loss, critical for multi-layered chips. Scalability allows adaptation to wafer sizes up to 450mm, meeting mass production demands. Versatility comes from modular designs that support both chemical and plasma etching. For instance, Tokyo Electron’s systems offer configurable gas mixtures to handle diverse materials like silicon, oxides, and metals. These characteristics make chip etching machines vital for fabricating advanced nodes in 5nm and below processes.
Selecting a chip etching machine requires evaluating parameters such as etch rate, uniformity, and selectivity. Etch rate determines throughput, while uniformity ensures consistent results across wafers. Selectivity—the ability to target specific materials—minimizes damage to underlying layers. Advanced systems also monitor real-time parameters like plasma density and ion energy. For example, ASML’s tools use sensors to adjust conditions dynamically, optimizing performance. These metrics directly impact yield and cost-efficiency, making them critical for procurement teams.
In semiconductor manufacturing, chip etching machines serve two primary roles: pattern transfer and material removal. During photolithography, etched patterns define transistor gates and interconnects. Post-deposition, etching removes excess material to isolate components. This dual function ensures chips meet electrical and thermal specifications. As devices shrink, the role of chip etching machines expands to include 3D structuring for memory cells like NAND flash. Such advancements underscore their irreplaceability in cutting-edge fabrication.
Chip etching machines are pivotal across industries:
Emerging applications include quantum computing and flexible electronics, where etching enables novel architectures. For example, Intel uses advanced etching to build stacked transistors for AI accelerators.
Leading chip etching machine manufacturers include:
These firms invest heavily in R&D to address challenges like edge placement error and line-edge roughness, ensuring their tools meet next-gen demands.
From enabling nanoscale circuits to powering global tech innovation, chip etching machines remain the backbone of semiconductor manufacturing. Procurement and engineering teams must prioritize parameters, applications, and vendor expertise when selecting these systems. As the industry advances toward 2nm nodes and beyond, the role of chip etching machines will only grow more critical.




Site Map | 萨科微 | 金航标 | Slkor | Kinghelm
RU | FR | DE | IT | ES | PT | JA | KO | AR | TR | TH | MS | VI | MG | FA | ZH-TW | HR | BG | SD| GD | SN | SM | PS | LB | KY | KU | HAW | CO | AM | UZ | TG | SU | ST | ML | KK | NY | ZU | YO | TE | TA | SO| PA| NE | MN | MI | LA | LO | KM | KN
| JW | IG | HMN | HA | EO | CEB | BS | BN | UR | HT | KA | EU | AZ | HY | YI |MK | IS | BE | CY | GA | SW | SV | AF | FA | TR | TH | MT | HU | GL | ET | NL | DA | CS | FI | EL | HI | NO | PL | RO | CA | TL | IW | LV | ID | LT | SR | SQ | SL | UK
Copyright ©2015-2025 Shenzhen Slkor Micro Semicon Co., Ltd