Service hotline
+86 0755-83044319
release time:2025-05-10Author source:SlkorBrowse:10068
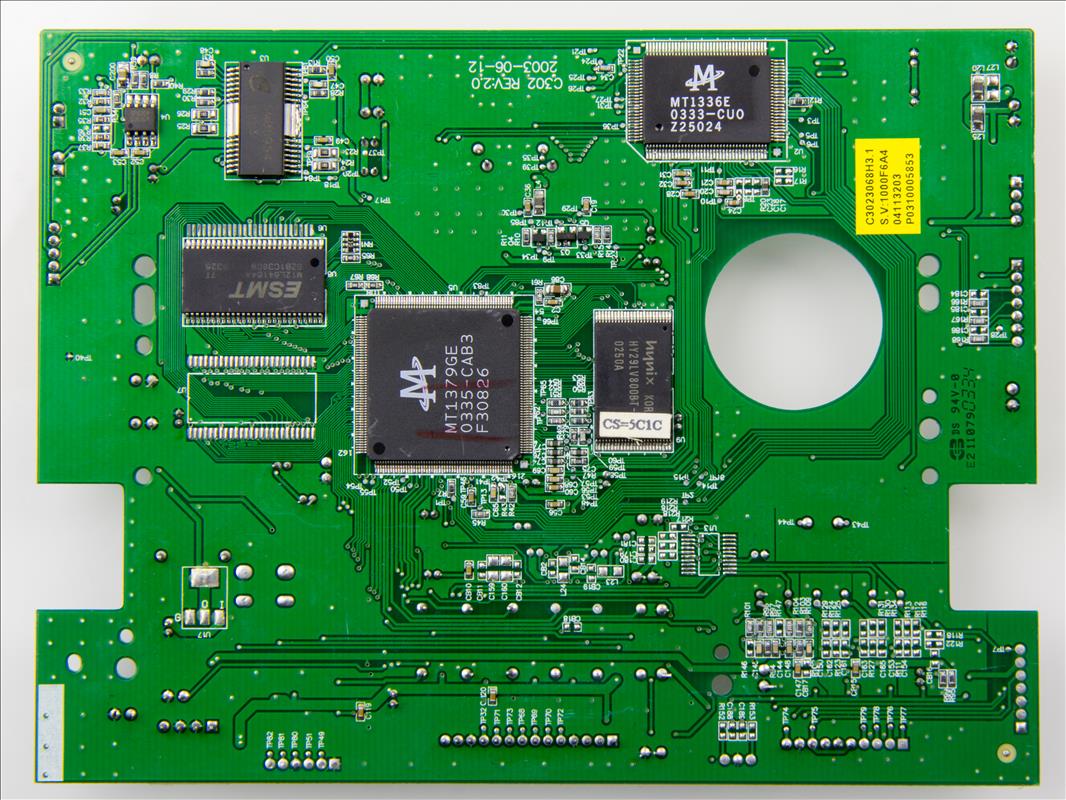
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) serves as the backbone of modern electronic devices, providing mechanical support and electrical connectivity for components. These boards are constructed from non-conductive substrates, such as fiberglass, layered with conductive copper traces. For procurement and engineering teams in consumer electronics, understanding PCB design and functionality is critical to optimizing product performance and cost-efficiency. From smartphones to industrial machinery, PCBs enable compact, reliable circuitry essential for today’s technology.
The evolution of PCB technology dates back to the early 20th century. Initially, circuits relied on bulky wiring, but advancements during World War II accelerated innovation. By the 1950s, companies like the U.S. Army pioneered multilayer boards, while the 1980s saw surface-mount technology (SMT) revolutionize miniaturization. Today, high-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs dominate industries requiring precision, such as medical devices and aerospace. This progression underscores the importance of staying updated on manufacturing trends for sourcing teams.
PCBs are defined by their material composition, layer count, and thermal resilience. Common substrates include FR-4 epoxy, while flexible boards use polyimide for bendable applications. Key parameters like PCB thickness, copper weight, and dielectric constant impact performance in high-frequency environments. Engineers prioritize these traits to ensure compatibility with devices ranging from wearables to automotive systems.
The choice of substrate and conductive layers determines a PCB’s durability and signal integrity. For instance, ceramic-filled boards excel in thermal management, making them ideal for power electronics.
Critical specifications for PCB selection include:
Procurement teams must collaborate with manufacturers to align these parameters with project requirements, balancing cost and performance.
Beyond connectivity, PCBs enhance signal integrity, reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), and streamline mass production. Their modular design allows rapid prototyping, which is vital for engineering teams aiming to shorten development cycles. For example, multi-layer PCBs in smartphones enable advanced features like 5G connectivity without compromising size.
From consumer gadgets to renewable energy systems, PCBs are ubiquitous. Key sectors include:
For deeper insights into industry standards, refer to the IPC website, a leading authority on electronics manufacturing.
Selecting reliable PCB suppliers is crucial for quality assurance. Leading companies like TTM Technologies and Jabil specialize in high-volume production, while niche firms cater to prototypes. Procurement teams should evaluate certifications like ISO 9001 and UL listing to mitigate risks.
Understanding PCB technology is indispensable for professionals in consumer electronics. By mastering its history, characteristics, and applications, procurement and engineering teams can make informed decisions that drive innovation and cost-efficiency. As the industry evolves, staying ahead of trends ensures competitive advantage in a rapidly changing market.




Site Map | 萨科微 | 金航标 | Slkor | Kinghelm
RU | FR | DE | IT | ES | PT | JA | KO | AR | TR | TH | MS | VI | MG | FA | ZH-TW | HR | BG | SD| GD | SN | SM | PS | LB | KY | KU | HAW | CO | AM | UZ | TG | SU | ST | ML | KK | NY | ZU | YO | TE | TA | SO| PA| NE | MN | MI | LA | LO | KM | KN
| JW | IG | HMN | HA | EO | CEB | BS | BN | UR | HT | KA | EU | AZ | HY | YI |MK | IS | BE | CY | GA | SW | SV | AF | FA | TR | TH | MT | HU | GL | ET | NL | DA | CS | FI | EL | HI | NO | PL | RO | CA | TL | IW | LV | ID | LT | SR | SQ | SL | UK
Copyright ©2015-2025 Shenzhen Slkor Micro Semicon Co., Ltd