Service hotline
+86 0755-83044319
release time:2022-04-20Author source:SlkorBrowse:8750
TVS全称是 transient voltage suppressor,A transient voltage suppressor whichIt is a protection device. TVS tube also belongs to diode, but its characteristics are different from those of diode. Its working principle is similar to that of zener diode, and it also uses reverse breakdown to stabilize voltage, but the response speed of TVS tube is faster than that of zener diode.
When the TVS tube in the circuit is impacted by the reverse transient high energy, it can run at a very high speed.(Hundreds of picoseconds)The impedance between the two stages is changed into low impedance, which plays a good role in absorbing surge power, and at the same time, the voltage between the two stages can be kept within a range, thus effectively protecting other components in the circuit from the damage of surge pulse.
The comparison between TVS tube and ZenerDiode can refer to the following description
一、similarity
1)The voltage of the device can be limited in a certain range.
2)The long-term current endurance value is close, which is related to the volume power consumption.
二、differentia
1)Voltage accuracy, ZenerDiode's regulated value is relatively accurate, and TVS is within a range;
2)Current capacity, ZenerDiode's surge resistance current is very small, while TVS can reach several hundred A;
3)Working principle: ZenerDiode is Zener tunnel effect or avalanche effect, and TVS is avalanche effect;
4)Circuit, ZenerDiode for voltage stabilization, TVS for transient high voltage protection;
5)Voltage stabilizing value, ZenerDiode 3.3V~75V,TVS tube 6.8V~550V;
6)The response time of ZenerDiode is us level, and TVS can reach 1ps level.;
After comparison, it is clear that zener diode and TVS tube can't replace each other.
To understand the principle, let's look at some parameters of TVS tube. We look at them through Datasheet, which is more intuitive.
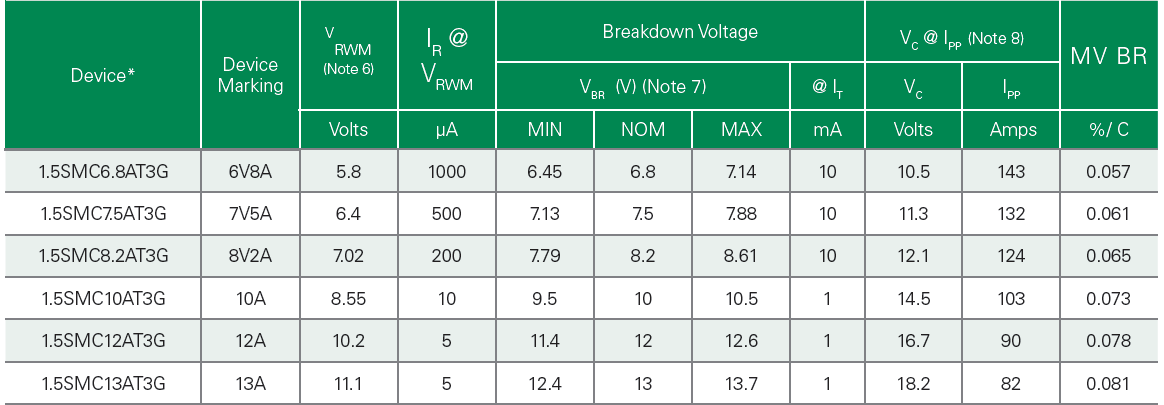
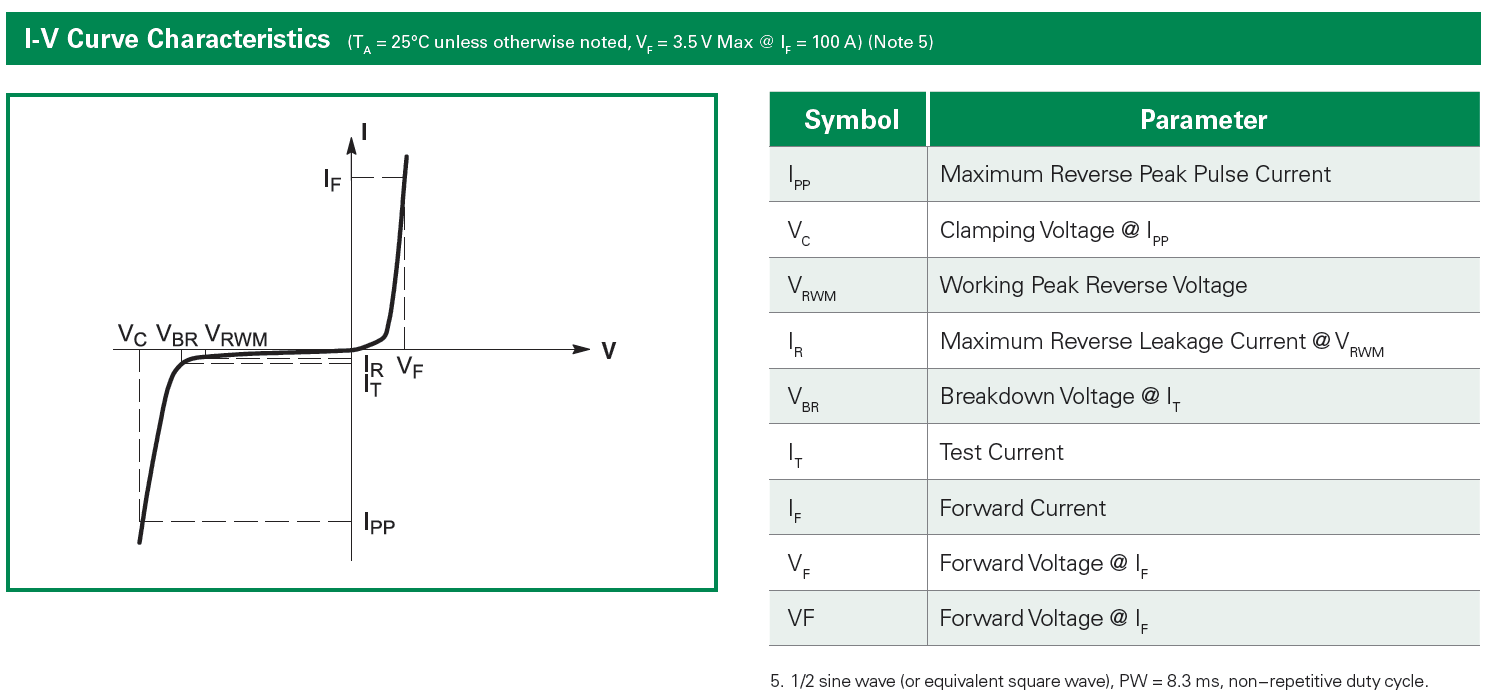
The first column and the second column are related to specific devices, and we don't care about it.
Working PeakReverse Voltage VRWM (V)Peak voltage, this parameter is the working voltage of TVS tube. When the device works normally, the resistance at both ends of TVS tube is very high, so the current absorbed by TVS tube can be neglected. Generally, VRWM is required to be equal to or slightly larger than the normal operating voltage of the circuit.
Breakdown Voltage VBR(V) MIN &NOM&MAX @IT Is the reverse breakdown voltage, which means that the reverse voltage across TVS is measured under the condition of DC current IT, which means that from this point on, the components enter the reverse avalanche breakdown.
Test Current IT(mA) Test current parameter is the condition that specifies the reverse breakdown voltage value of TVS.;
Claping Voltage @IPP Vc(V)Maximum clamping voltage parameter, the maximum voltage applied to the device when TVS bears the maximum peak current Ipp within the specified pulse time tr/tp.
Maximum Peaking Pulse Current IPP(A) Maximum pulse current, the maximum peak pulse current allowed by the device in the specified time tr/tp.
Reverse Leakage @VRWM IR(uA) Reverse leakage current, that is, the reverse leakage current flowing through TVS tube at the working voltage VRWM.
In addition, insert loss @ Freq will be given on datasheet, which is mainly used for TVS protected on high-speed IO, as an important basis for selection.
After knowing the above parameters, the next step is the selection process. The information obtained from the Internet, the selection principle is
1)The rated reverse turn-off voltage VRWM of TVS should be greater than or equal to the maximum working voltage of the protected circuit.
2)Minimum breakdown voltage VBR=VWM/KBR (where KBR = 0.8 ~ 0.9).
3)The maximum clamping voltage VC of TVS should be less than the damaged voltage of the protected circuit, that is, VC=KC×VBR (where KC=1.3).
④ Within the specified pulse duration, the maximum peak pulse power consumption PM of TVS must be greater than the peak pulse power that may occur in the protected circuit. After the maximum clamping voltage is determined, the peak pulse current should be greater than the transient surge current.
The following is an example calculation analysis.:
The working voltage of a machine is DC12V, the maximum allowable safe voltage is 25V (peak value), the impedance of surge source is 50MΩ, its interference waveform is square wave, TP=1ms, and the maximum peak current is 50A. select:
1、First, the maximum reverse working voltage VRWM is 13V from the working voltage of 12V, which means that it can work normally at this voltage.
Then breakdown voltage V(BR) =VRWM /KBR=13/0.85=15.3V(getKBR=0.85)
Under the breakdown voltage of 15.3V, TVS starts to operate.
2、Then, according to VBR, the maximum clamping voltage Vc(MAX)=1.30×V(BR)=19.89V, Vc=20V (KC=1.3), which means the maximum voltage applied to the device under certain conditions (when the pulse time tr/tp is the maximum peak current Ipp).
3、Then according to the clamping voltage VC and the maximum peak current IP, the square wave pulse power is obtained.:
PPR=VC×IP=20×50=1000W
4、Equivalent to the peak power of TP=1msS exponential wave with TP = 1, and the equivalent coefficient K1=1.4,
PPR=1000W÷1.4=715W
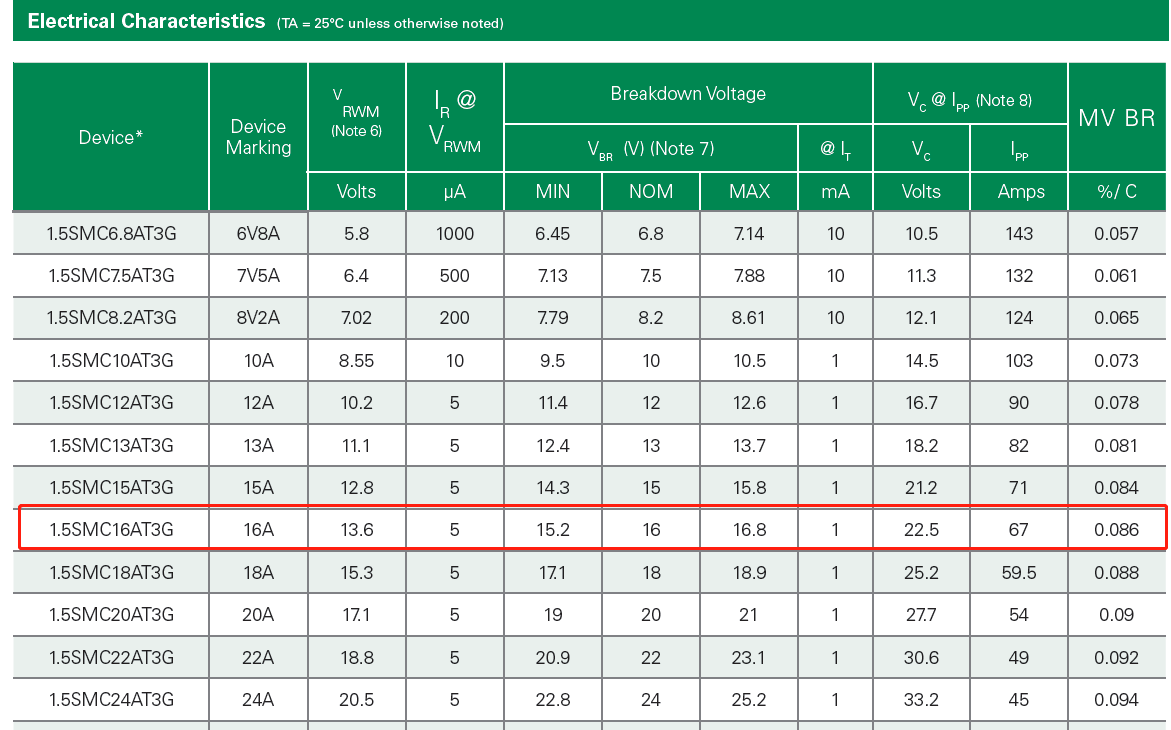
1.5SMC16AT3G can be found from the manual, where PPR=1500W, displacement voltage VRWM=13.6V, breakdown voltage V(BR)=15.2V, maximum clamping voltage Vc=22.5V,
Maximum surge current IP=67A. It can meet the above design requirements, and has a double margin, which is suitable for both square wave and exponential wave.
(The content of this article is picked from the Internet, and opinions and opinions do not represent the position of this site. If there is infringement, please contact us to delete it!)



Site Map | 萨科微 | 金航标 | Slkor | Kinghelm
RU | FR | DE | IT | ES | PT | JA | KO | AR | TR | TH | MS | VI | MG | FA | ZH-TW | HR | BG | SD| GD | SN | SM | PS | LB | KY | KU | HAW | CO | AM | UZ | TG | SU | ST | ML | KK | NY | ZU | YO | TE | TA | SO| PA| NE | MN | MI | LA | LO | KM | KN
| JW | IG | HMN | HA | EO | CEB | BS | BN | UR | HT | KA | EU | AZ | HY | YI |MK | IS | BE | CY | GA | SW | SV | AF | FA | TR | TH | MT | HU | GL | ET | NL | DA | CS | FI | EL | HI | NO | PL | RO | CA | TL | IW | LV | ID | LT | SR | SQ | SL | UK
Copyright ©2015-2025 Shenzhen Slkor Micro Semicon Co., Ltd